This case study introduces the stress assessment of two caissons: a sea water dump caisson with a 1000mm diameter header to which seven smaller diameter nozzles were attached, and a produced water caisson with a diameter of 400mm and three connecting lines.
Analysis
The loads on the lines connecting to the caissons were supplied by the client. In this analysis, the required wall thickness of the caissons and the geometries of the laminates at the nozzle intersections were calculated. The assessment utilized both the pipe modeling package CAESAR II and the finite element package FE Pipe.
For the smaller 400mm diameter caisson, the nozzle geometry was simpler, allowing for a simplified approach using a 1-D piping model in CAESAR II. Here, the effect of the nozzle-header interface was accounted for using the SIF (Stress Intensification) values, which conformed with the ISO 14692 standard.
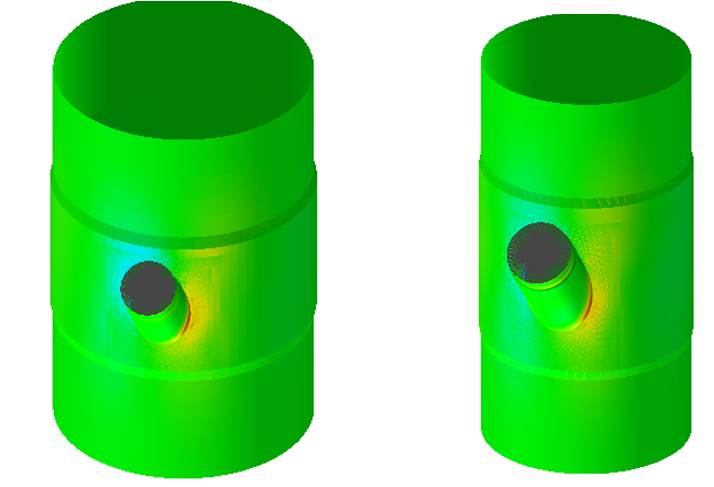
Results
The loads supplied by the client led to stresses at the nozzle/caisson interfaces far exceeding the allowable stress envelope if standard pipe pressure ratings and laminate procedures were used. Therefore, after discussion with the client, the pressure ratings of the connecting pipes were significantly increased. The laminate thicknesses were also increased compared to standard practice. These modifications ensured that stresses in the nozzle/caisson intersections were within the allowable stress envelope and in conformance with the ISO 14692 standard.
Additionally, restraint forces on the supports of the caissons were calculated and provided to the client. A check was also made to confirm that the laminates used to join the sections of the laminate together were within allowable limits.
Key Takeaways
- Stress assessments are crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of GRP caissons and nozzle intersections.
- Pipe modeling software like CAESAR II and FE Pipe can accurately analyze stresses in complex piping configurations.
- Nozzle/caisson intersections are critical areas where stresses may exceed allowable limits.
- Increasing pipe pressure ratings and laminate thicknesses can mitigate high stresses at intersections.
- Conformance with design codes like ISO 14692 is essential for safe and reliable operation.
- Close collaboration between stress analysts and clients is vital for effective design modifications.






