Introduction
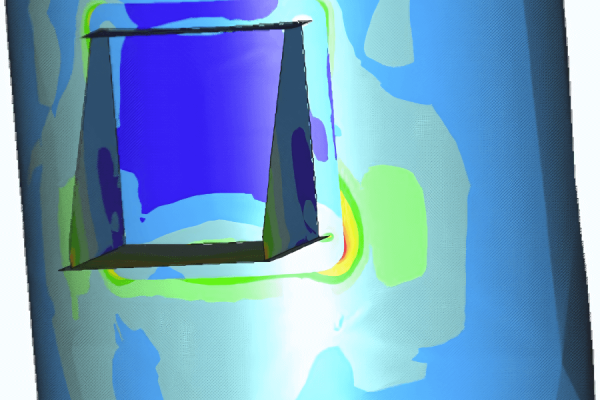
In this case study, a finite element stress analysis was conducted on a seawater dump caisson installed on the deck of a floating offshore structure in the North Sea. The caisson comprises a 56” (ID1400) Glass Reinforced Epoxy (GRE) pipe header, fixed at the main deck and guided at the upper deck. At the upper section of the caisson header, two process nozzles are attached: a 30” (ID750) nozzle and a 16” (ID400) nozzle. Additionally, a 24” vent nozzle is installed in the cover plate closing the top part of the caisson.
Analysis
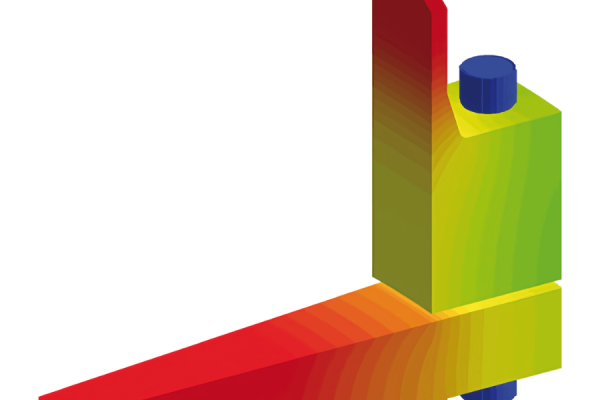
For the analysis, a finite element (FE) model was constructed based on the design conditions, provided drawings, and nozzle loads. The model focused on the top section of the caisson and was truncated at the guide location, with relevant boundary conditions assumed.

This model was used to determine the interface stresses between the nozzles and pipe header and the overall stress in the caisson header.
Results
Two details of the caisson were studied: the discontinuity stresses at the header/nozzle interfaces of all nozzles and the overall stresses in the header pipe between guide and fixation.
“The results of the analysis described the optimal GRE pipe and laminate thickneses to accommodate the prescribed loads.”
From the received loads three load cases were identified: sustained, operational, and occasional which form the basis of the FE analysis.
From the analysis the following conclusions were drawn:
- When the prescribed changes were applied, all stresses stayed within the allowable limits of the ISO 14682 code.
- Furthermore, it was recommended to increase the steel ring shoe of the caisson guide support and apply a neoprene wrapping between the steel ring and GRE header to allow for a smooth transfer of the loads from pipe to guide.